Foliar Symptomology, Nutrient Content, Yield, and Secondary Metabolite Variability of Cannabis Grown Hydroponically with Different Single-Element Nutrient Deficiencies
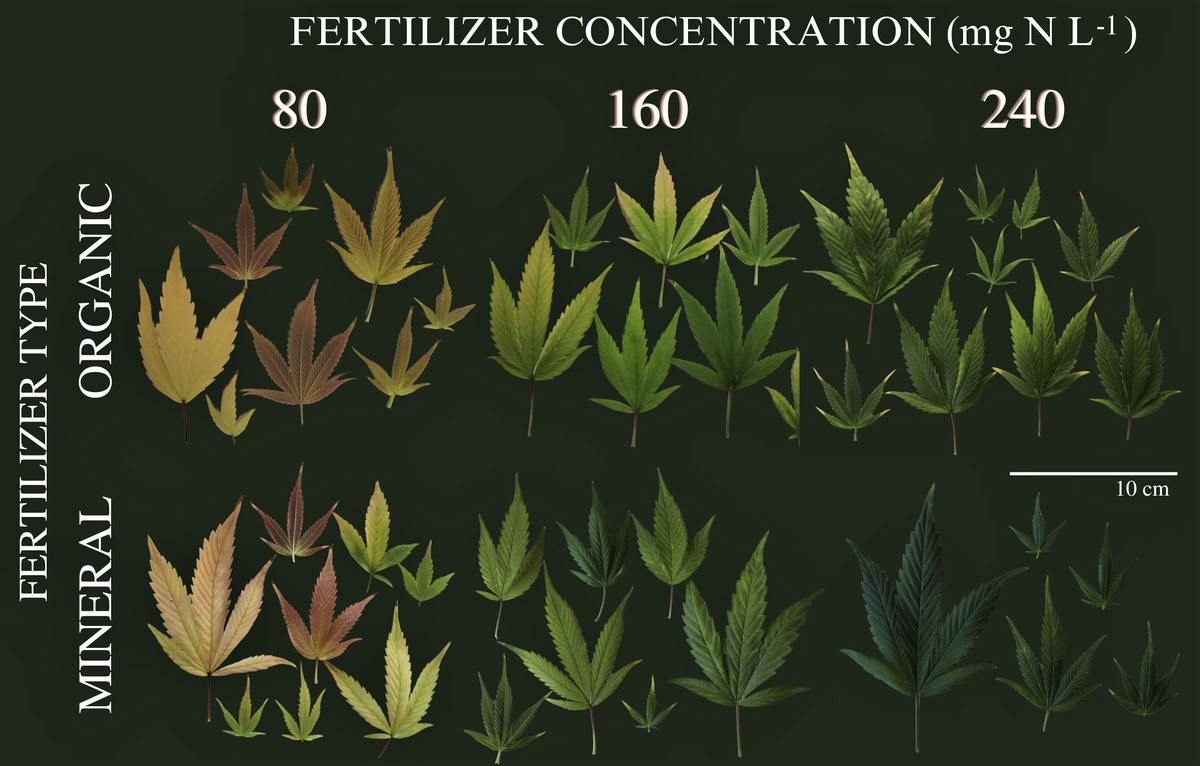
In controlled environment production systems, Cannabis sativa (hereafter cannabis) is a commodity with high nutrient demands due to prolific growth under optimized environmental conditions. Since nutrient deficiencies can reduce yield and quality, cultivators need tools to rapidly detect and...
Optimisation of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium for Soilless Production of Cannabis sativa in the Flowering Stage Using Response Surface Analysis - PMC
Following legalisation, cannabis has quickly become an important horticultural crop in Canada and increasingly so in other parts of the world. However, due to previous legal restrictions on cannabis research there are limited scientific data on the ...
Plant_nutrition
Plant_nutrition the macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) the micronutrients (or trace minerals): iron (Fe), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nic...

5.1: Brønsted–Lowry Acids and Bases

Periodic Table of the Elements
THIS SHEET ABOVE WILL INCLUDE TARGET LEVEL OF NUTES FOR CANNABIS
SOURCES WILL BE SOIL TEST AND IDENTIFIED DEFICIENCY AS WELL AS TEST CASES
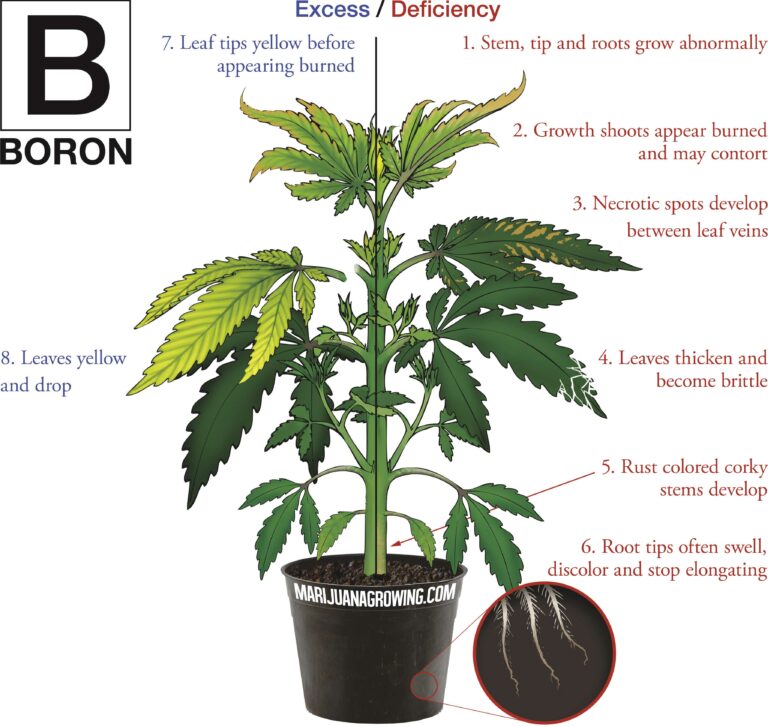
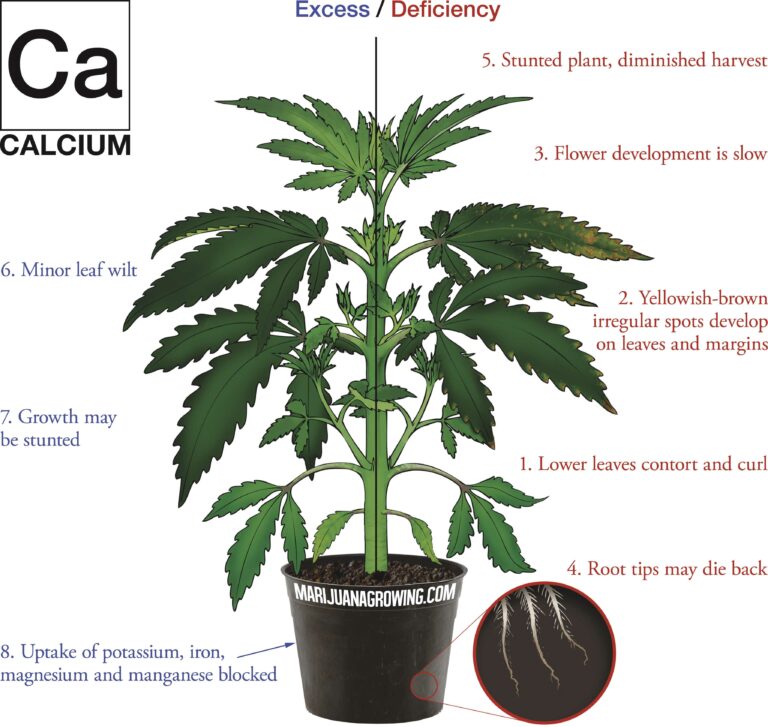
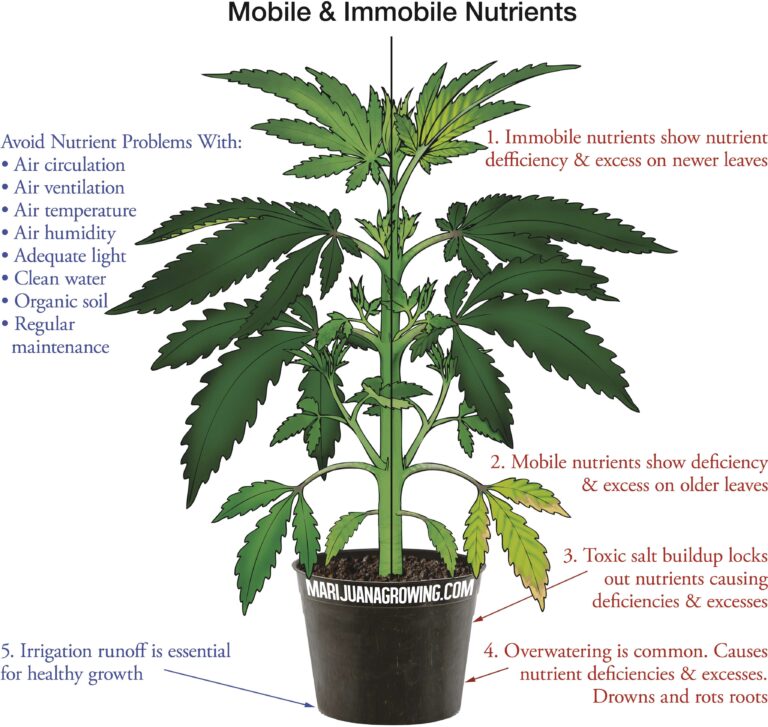
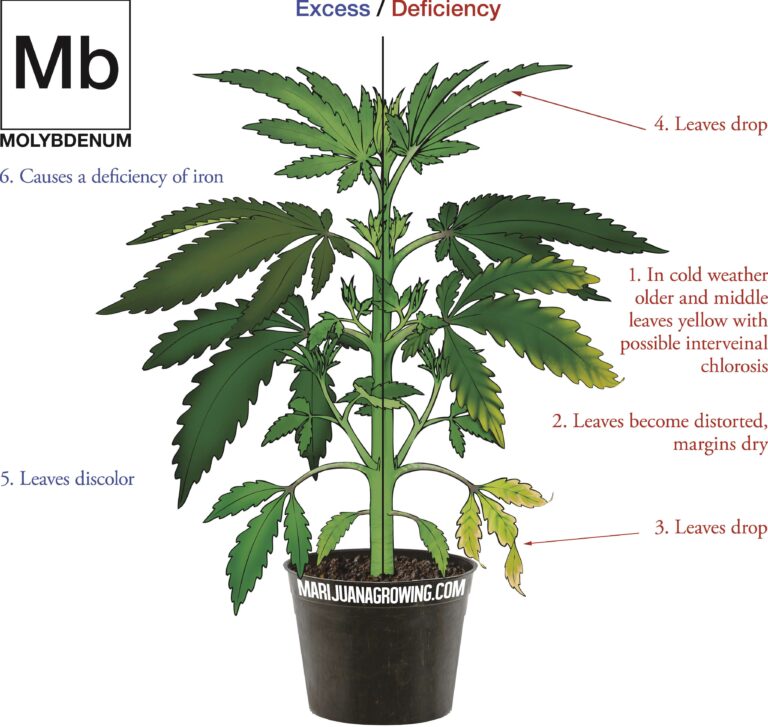
A visual guide to cannabis deficiencies
A visual guide to cannabis deficiencies Many growers look for the ‘secret’ to growing the best possible cannabis. In reality there is no single secret, instead there are some basic principles. Your plants need to be kept in the right temperature/humidity range, with a suitable light, climate and ...

A visual guide to cannabis deficiencies
Worried about your plant health? See a cannabis deficiency that you cannot identify? Our guide to cannabis deficiencies may help you solve your problems
"The availability of the most abundant nutrient in the soil is only as good
as the availability of the least abundant nutrient in the soil."
MY PRIMARY INTEREST IS IN ORGANICS WILL LIST SOME THREADS BELOW THIS LINE TO KNOWLEDGEABLE HYDRO ICers
IN BEST PRACTICES ITS BEST TO TEST SOIL AND SOLUTION,
UNDERSTANDING YOUR SOIL / SOLUTION TESTS
Mehlich-1 (Dilute Double Acid)
Mehlich-1, or the dilute double-acid extractant, is one of the earliest versions of "universal" soil extractants (single chemical reagent that can extract all the essential plant nutrients), and is especially suited for the acidic, low organic matter, mineral soils of the southeastern United States. Adopting the M1 procedure enabled universal extraction of all standard plant nutrients in the soil sample, including P, K, Ca, Mg, Zn, Cu, Mn, and B. The M1 extractant is composed of two dilute acids: 0.05M HCl and 0.0125M H2SO4 (Table 1). Mehlich-1 was the soil extractant used as the standard method by the UF/IFAS Extension Soil Testing Laboratory for acidic-mineral soils in the state. This extractant is well designed for soils in the acidic pH range with low CEC (Mylavarapu and Miller 2014).
However, M1 should not be used to extract neutral or alkaline soils. When exposed to a neutral or alkaline pH soil, M1 rapidly loses effectiveness because the dilute acids are effectively neutralized. M1 is also rendered ineffective in soils with high cation exchange capacity (CEC), high Al and Fe accumulation, and high organic matter (>5%) content.
Mehlich-3 (M3)
In order to overcome the limitations of M1, Mehlich improved the chemistry and developed the Mehlich-3 (M3) extraction solution (Mehlich 1984). In the M3 extractant, the two dilute double acids used in M1 have been replaced with 0.2M CH3COOH, 0.015M NH4F, 0.013M HN03, 0.001M EDTA, and 0.25M NH4N03. Presence of 0.001M EDTA essentially enhanced the extraction of micronutrients, particularly Cu. It was expected that this extractant would also make the extraction of Mn and Zn consistent and result in a better correlation with plant uptake. In the M3 development process, emphasis was placed on detection of micronutrient deficiencies compared with toxicities. Soil sample pH in the acidic range of pH ~ 2.5 (accomplished through the addition of 0.2M CH3COOH) was required during the M3 extraction process to take advantage of the fluoride component. A pH of 2.5 helped prevent reaction of Ca and F to form a CaF2 precipitate. The fluoride facilitated the extraction of phosphates associated with Fe and Al while ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) effectively extracted exchangeable cations. State extension laboratories in several southern US states have since moved to the M3 extraction procedure because of its improved efficiency (particularly for micronutrients) and its broad range of applicability (slightly beyond neutral pH) (Zhang et al. 2014). Also, the M3 procedure has been the only soil test extraction method that has been validated through interlaboratory studies for extraction of plant-available phosphorus and used as a reference method for testing soil materials for extractable P (Zhang et al. 2009).
place soil in jar with water and shake settle view horizons
Attachments
Last edited: