A de Finetti diagram. The curved line is the expected Hardy–Weinberg frequency as a function of p.
A de Finetti diagram is a ternary plot used in population genetics. It is named after the Italian statistician Bruno de Finetti (1906–1985) and is used to graph the genotype frequencies of populations, where there are two alleles and the population is diploid. It is based on an equilateral triangle, and Viviani's theorem: the sum of the perpendicular distances from any interior point to the sides of said triangle is a constant equal to the length of the triangle's altitude.
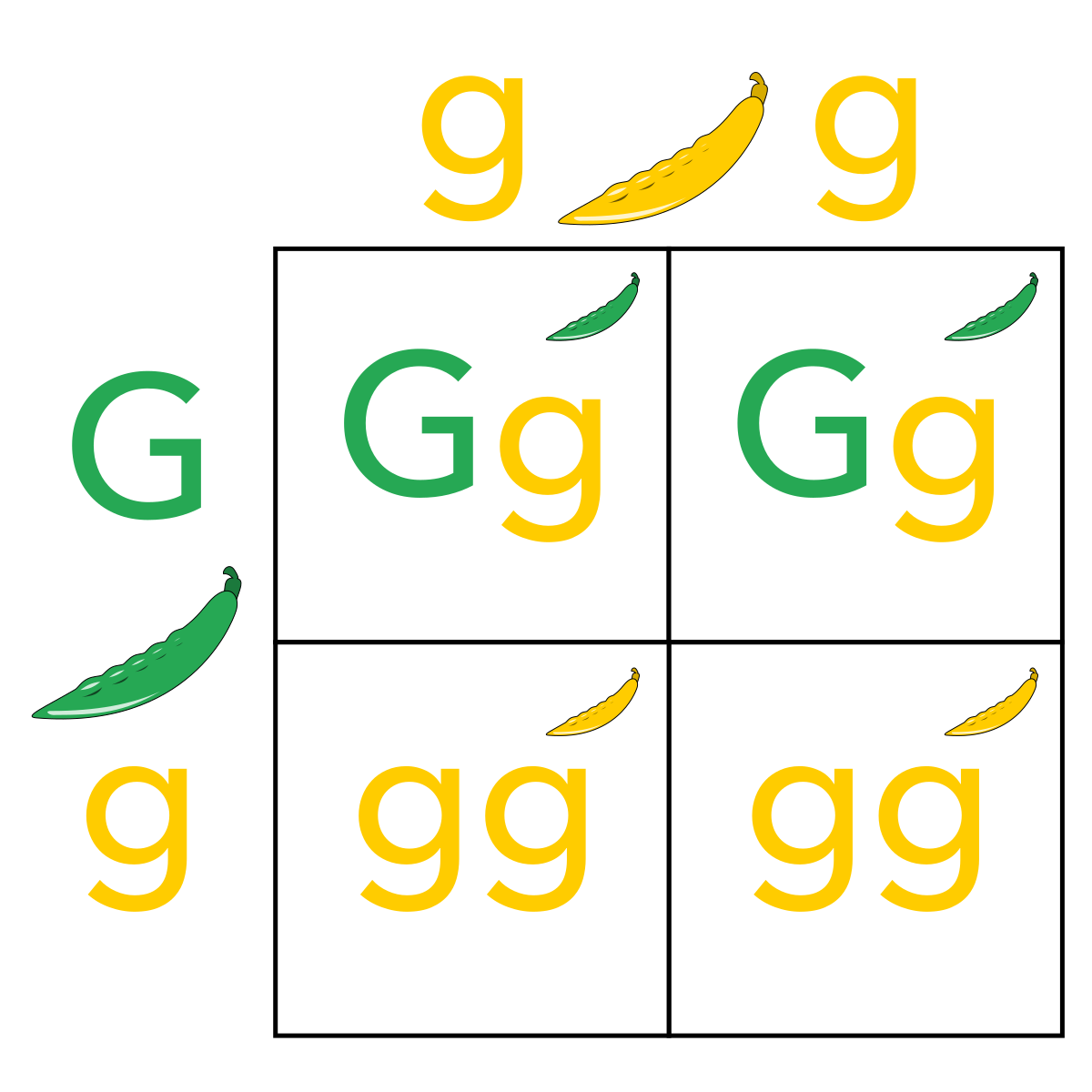
Example: Autosomal dominant trait

The diagram shows the inheritance of freckles in a family. The allele for freckles (F) is dominant to the allele for no freckles (f).
At the top of the pedigree is a grandmother (individual I-2) who has freckles. Two of her three children have the trait (individuals II-3 and II-5) and three of her grandchildren have the trait (individuals III-3, III-4, and III-5).
[What is the genotype of individual I-2?]
Example: X-linked recessive trait
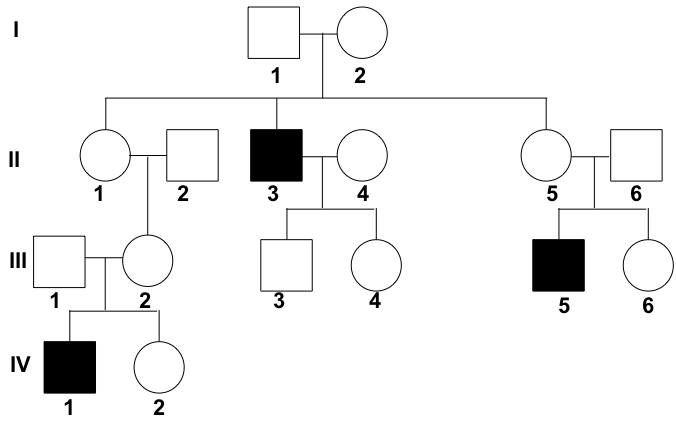
The diagram shows the inheritance of colorblindness in a family. Colorblindness is a recessive and X-linked trait (Xb)(X�). The allele for normal vision is dominant and is represented by XBX�.
In generation I, neither parent has the trait, but one of their children (II-3) is colorblind. Because there are unaffected parents that have affected offspring, it can be assumed that the trait is recessive. In addition, the trait appears to affect males more than females (in this case, exclusively males are affected), suggesting that the trait may be X-linked.

6.2: Pedigrees review
By analyzing a pedigree, we can determine genotypes, identify phenotypes, and predict how a trait will be passed on in the future. The information from a pedigree makes it possible to determine how certain alleles are inherited: whether they are dominant, recessive, autosomal, or sex-linked.
SNP 1 | SNP 2 | SNP 3 | SNP 4 | SNP 5 | SNP 6 | SNP 7 | SNP 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sample 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sample 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Sample 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Sample 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sample 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
In population genetics, the allele frequency spectrum, sometimes called the site frequency spectrum,
is the distribution of the allele frequencies of a given set of loci (often SNPs) in a population or sample.
Allele frequency spectrum - Wikipedia
Full size table
Fig. 1
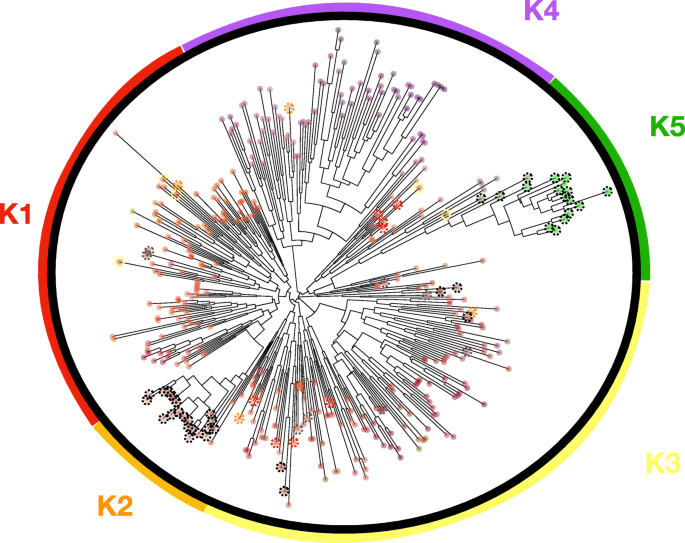
Neighbour-joining tree. Showing the relative phylogenetic location of the 420 cannabis accessions typed at 23 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). Discriminant analysis of principal component (DAPC) clusters are shown with K1-K5 represented by different colors. K1-K4 are resin type cannabis and K5 is the fiber type cannabis or hemp. Colored dotted circles highlight individuals assigned differently between the neighbor-joining tree and DAPC clusters. Type-III plants are shown with a dotted black circle and type-II plants are shown with dotted grey circle
Full size image
Fig. 2
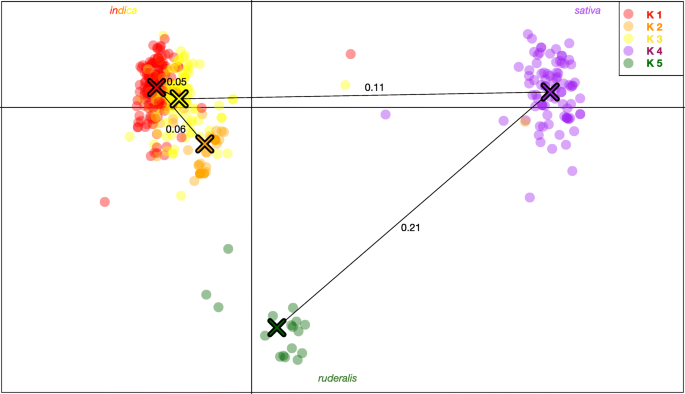
Discriminant analysis of principal component (DAPC) scatterplot. Showing the relative location of each individual sample in two dimensional space, overlaid by a minimum spanning tree calculated from the squared distance between individual to represent the phylogenetic relationship between inferred clusters. K5, hemp or “ruderalis” appears ancestral and the most differentiated group, followed by K4, terpinolene dominant resin accessions. The genetic distance between groups (Fst) is indicated on the respective branches of the minimum spanning tree
https://jcannabisresearch.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s42238-020-00036-y/figures/2
J Cannabis Res
. 2020 Sep 11;2:26. doi: 10.1186/s42238-020-00036-y
A single nucleotide polymorphism assay sheds light on the extent and distribution of genetic diversity,
population structure and functional basis of key traits in cultivated north American cannabis
Last edited: